Assembly inspection using industrial computed tomography scanning
Assembly analysis and component inspection with 3D X-ray inspection
Defective seals, incorrectly assembled or missing components often remain undetected in a conventional visual inspection or 2D X-ray inspection. Industrial computed tomography scanning (CT) generates a detailed volume model of your assembly and enables non-destructive assembly inspection in the µm range. This enables manufacturers in the automotive, aerospace, and medtech sectors to ensure that every part is assembled correctly and that functionally critical components have been checked without dismantling. We are happy to offer you a screening inspection.
Core functions of 3D X-ray inspection for assembly control
| Your advantages: |
|---|
| Interior view of all joints and assembly errors detected without disassembly |
| 3D color heat map (nominal / actual) deviations in bearings, fits, and sealing surfaces are immediately visible |
| Support structures in AM components are detected and chips or powder residues remaining in the component are identified |
| Screening inspection possible, can also be automated depending on the desired focus area. Batch-wise good/bad classification directly from the CT data |
| CT services provided by accredited testing laboratory (DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2018) and accredited CT testing procedure (DIN EN 15708-3) |
Typical application scenarios

Valve assemblies with seals:
Seals and O-rings can be checked volumetrically for accuracy of fit and seating while assembled, without dismantling the assembly. Air and fluid leaks can thus be ruled out at an early stage.
Encapsulated electronic modules:
In the case of encapsulated/bonded control units, industrial CT scanning reveals trapped air bubbles, solder joint breaks, or faulty wire bonds that 2D X-ray imaging can only partially detect due to overlaps or a lack of cross-sectioning options.
Materials that can be tested using CT
Industrial computed tomography scanning enables the non-destructive measurement of components made from many materials used in the automotive, medical technology, and aerospace industries. Examples:
- Aluminum and magnesium die casting
- Titanium and Inconel for additively manufactured components
- Steel & sintered metal
- Polymer housings (PA, PEEK, PC)
- Ceramic substrates and glass bodies
- Printed circuit boards, soldered and bonded connections
- Sealing and elastomer components
What you get from TPW CTinspect:

- Digital image data: 3D volume data set (.vgl) or 2D sections (.jpg / .pdf)
- Screening inspection (optional): Good/bad marking of complete batches
- Recommendation of a free, very comprehensive viewer for your 3D data
- For questions about interpreting results: Technical discussion with a CT engineer
- Secure data transfer (server location in Germany) and password-protected access to your analysis data
- In consultation with you, if required: Analysis report (PDF) with tolerance & damage analysis
.
.
.
Further testing methods from TPW CTinspect
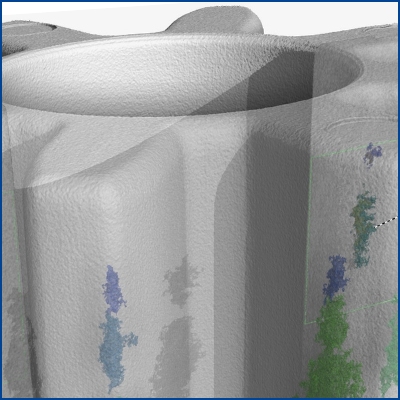
Cavity inspection / pore analysis
Identify gas inclusions, shrinkage, bonding defects, or hidden foreign particles — non-contact and non-destructive.
LEARN MORE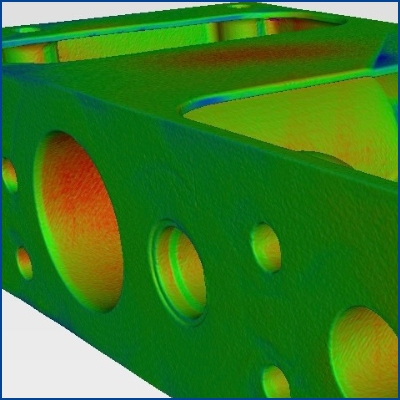
Nominal actual analysis
The nominal/actual comparison provides you with a color-coded CT scan that highlights deviations outside the tolerance range in color.
LEARN MORE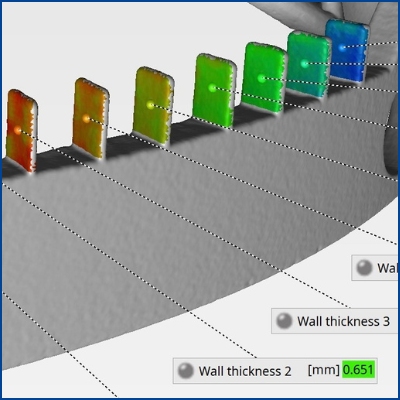
Wall thickness analysis and wall thickness measurement
Perform non-contact wall thickness measurement and identify tolerance deviations.
LEARN MORE